Introduction
Farming system are the various methods used to produce crop and animal products.
The various systems used in farming are geared towards the increase of crops and animal production. They must be well practiced for good results. The practices are chosen based on several factors.
In this topic, you will learn about the farming systems in Ghana.
Farming Systems
Farming systems refer to the ways by which farming activities are carried out. Farmers have ways of handling their farms. There are some farmers who grow one crop at a time. Others grow different crops on the same field at the same time. Other farmers grow and rear animals on the same field or on a different field. The ways by which a farmer manages his / her farm are referred to as farming system.
Some farming systems practiced in Ghana are:
Land rotation
Mixed farming
- Crop rotation
- Monocropping
- Shifting cultivation
- Pastoral farming
- Mixed cropping
- Monoculture
Land Rotation
This is a system of farming in which a farmer cultivates a piece of land for sometime and leaves it to clear a new land when the old land becomes less fertile. The farmer moves to the new land without moving his settlement.
Advantages
- The land regains lost nutrients after a fallow period (free period to regain fertility)
- It helps check the spread pests and diseases are reduced because the land is left for long time
Disadvantages
- This farming system needs a lot of time and work.
- Virgin forest is destroyed
- It does not encourage large scale farming.
Shifting Cultivation
This is a farming system whereby the farmer cultivates a piece of land for sometime and then moves his / her family and settlement away from the land when the soil loses its fertility. The land is allowed to fallow(left free to regain fertility)
Advantages
- It helps check the outbreak of pests and diseases.
- The land regains fertile again during the fallow period.
- Simple farm tools such as hoes, cutlasses and among others are used in this farming system.
Disadvantages
- Virgin forest is destroyed.
- It does not encourage large scale farming.
- It can not be practised at areas where demands on land is high.
- This farming system needs a lot of time and work.
Mixed Farming
Mixed farming is a farming system in which a farmer produces both animals and crops on the same farm at the same time.
Advantages
- The land is efficiently used
- Labourers are efficiently used
- Animals feed on crop residues and plants also need animals droppings for manure to grow well.
- The farmer can use the animals to help in some of the farm works such as ploughing
Disadvantages
- The farmer works throughout the year without rest.
- The animals can destroy the crops when they are not well kept.
- The farmer needs a lot of skills to handle both animals and crops properly
Crop Rotation
This is a farming system in which different types of crops are grown on a piece of land in a definite order or cycle season after season.
The farm is divided into several plots, and the crops which are grown are moved from plot to plot each year. This system preserves the fertility of the soil.
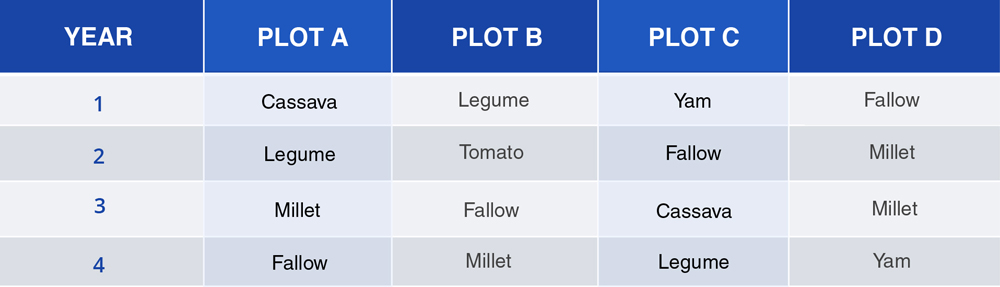
Advantages
- It controls soil erosion
- Maintain soil fertility
- It ensures effective use of labour
- Pests and diseases are controlled as crops are rotated.
- It helps to make maximum use of soil nutrients.
Disadvantages
- It is very difficult to adopt because of the skills required.
Importance of legumes in crop rotation
- They help in the control of soil erosion and weeds when used as cover crops.
- They improve nitrogen in the soil.
- They increase soil fertility.
- They improve the soil structure.
Monocropping
This is a system of farming in which a farmer cultivates one type of annual crop on a piece of land, at a time and changes after harvest.
Advantages
- Pests and diseases control are easily done
- The land is efficiently used
- Skills are obtained from this practice
Disadvantages
- It becomes a high risk system when the price of the crop falls at the market
Pastoral Farming
This is a farming system in which the farmer rears animals like sheep, cattle etc on a large scale and moves them from place to place in search of food and water.
Advantages
- The farmer can obtain meat or milk from the animals.
- The farmer can use the droppings for manures.
Disadvantages
- Excessive grazing will destroy the vegetation of the land.
- Over garzing will cause erosion.
- The animals could also be attacked by predators.
- There could be easy outbreak of diseases such as anthrax
Mixed Cropping
This is a farming system where a farmer grows two or more different type of crops on the same piece of land at the same time.
Advantages
- The farmer can select crops that will improve soil fertility.
- The dense canopy of the crops protects the soil against erosion.
- The farmer obtains a variety of crops from the farm.
- The farmer gets a balanced diet.
- Nutrients in the soil are utilized
- Spread of diseases is checked and prevented
Disadvantages
- Nutrients in the soil are used faster
- There is competition between crops for nutrients because the crops are different.
Monoculture
This is a farming system in which a farmer grows one type of annual or perennial crop on the same piece of land.
Advantages
- Cultural practices are easily carried out.
- The farmer selects the suitable implement for the cultivation of the crop.
- Crops are easily produced on large scale.
Disadvantages**
- Diseases and pests spread easily
- The farmer will always use dangerous erosion control measures.
Ecological farming
This is a system of farming in which the vegetation of the environment is not destroyed but rather protected.
Advantages
- It helps to reduce environmental degradation
- Pests are reduced
- It helps to reduce soil erosion.
- Environmental pollution is reduced
- It helps to improve the climate and environment.
Summary
Farming system deals with crop and animal production. There are eleven (11) main systems in Ghana.
They are; Monoculture, intensive farming, mixed farming, mixed cropping, pastoral farming, Mono cropping. Crop rotation, organic farming, land rotation, extensive farming and shifting cultivation.